Over the past two years, the healthcare industry has undergone a profound and rapid AI-driven transformation. Long considered slow to digitize and burdened by high technology implementation costs, the healthcare system is now scaling from pilot exploration to widespread adoption at a pace that exceeds expectations.

AI in Healthcare: A Comprehensive Update — Why Silicon Valley Has Produced the Most AI Unicorns in Healthcare
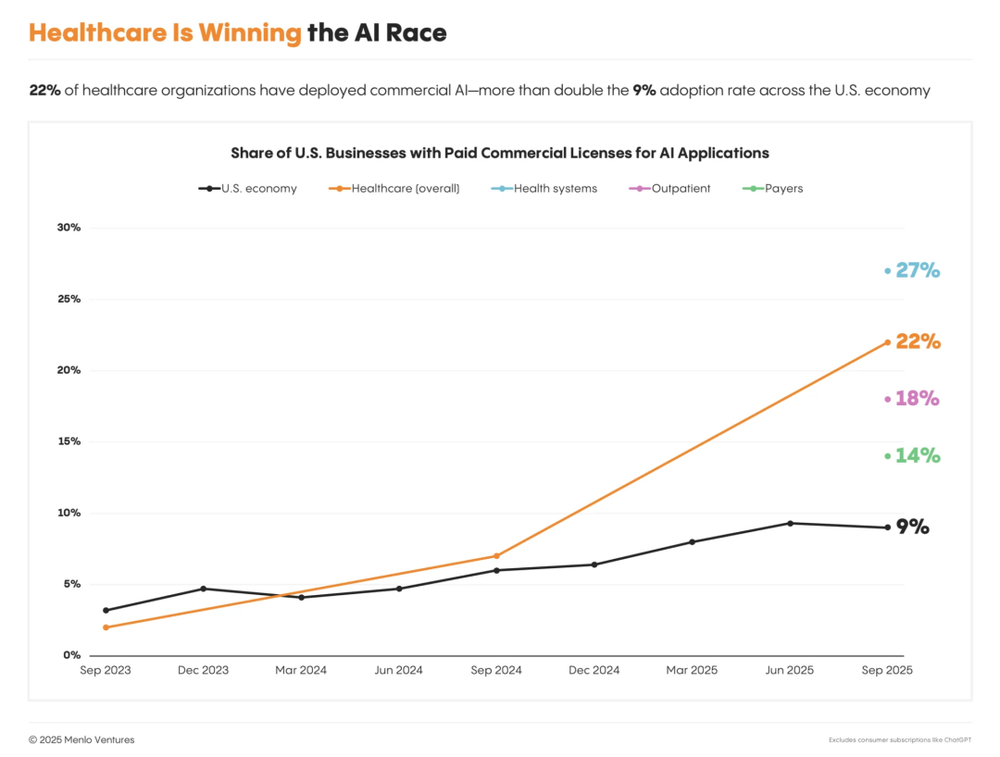
In the U.S.—a $4.9 trillion industry—AI adoption has surged from less than 3% to nearly 27% in just two years, making healthcare one of the sectors with the highest AI penetration. Large health systems, outpatient clinics, and payers are accelerating deployment, signaling that AI in healthcare has officially entered the “production-grade application” phase. The sector has already produced numerous emerging leaders and potential billion-dollar valuation players.
This Menlo Ventures report is based on a systematic survey of over 700 healthcare executives across the U.S., complemented by in-depth interviews with key industry figures, offering a comprehensive overview of AI’s implementation pathways and commercial logic in healthcare:
In 2025, annual investment in healthcare AI reached 1.4billion—nearlytriplethatof2024—withhealthsystemscontributingapproximately1 billion (75%).
Unlike previous healthcare IT initiatives, this wave of AI adoption exhibits clear "non-linear acceleration."
Of all generative AI spending in healthcare, 85% flows to startups, though most customers still prefer purchasing AI services through existing EHR platforms.
Providers represent the earliest, largest, and most ROI-clear application scenario for AI.
AI in payer operations remains early-stage but has already surpassed $50 million in scale, growing at a 5x annual rate.
01. Healthcare as a Key Engine Driving AI Commercialization
Historically, across multiple technology cycles, healthcare has been viewed as one of the slowest and most costly sectors for AI adoption. Fragmented service structures, complex compliance requirements, and outdated IT systems have often limited new technologies to localized pilots. However, this long-standing perception is rapidly shifting.
On one hand, breakthroughs in large language models have significantly lowered barriers to applying AI in natural language understanding, speech recognition, and complex decision support—enabling AI to finally address healthcare’s highly unstructured nature. On the other hand, real-world pressures like physician burnout, rising operational costs, and workforce shortages are forcing providers to actively seek efficiency-focused technologies as essential tools—not optional innovations.
As a result, AI adoption in healthcare now follows a markedly different path compared to traditional IT systems: deployment cycles are dramatically shorter, ROI is more clearly defined, and scalable implementations are already underway in high-frequency scenarios such as clinical documentation, revenue management, and patient interaction. The healthcare system is transitioning from a passive technology recipient to a critical engine driving AI commercialization.
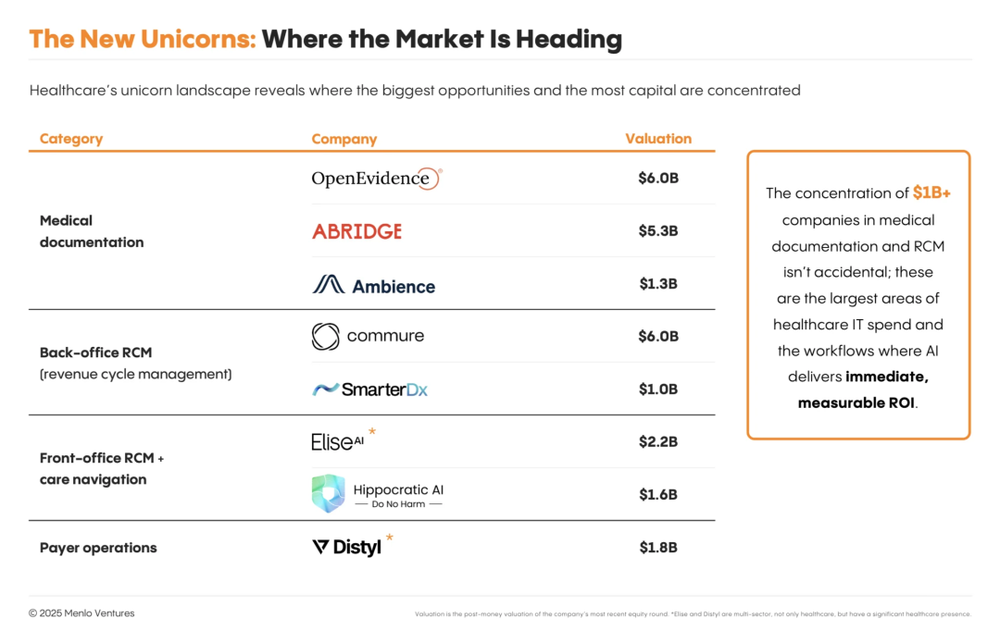
In 2025, annual investment in healthcare AI hit 1.4billion—nearlytriple2024’sfigure.Bycomparison,totalAIinvestmentinotherverticalslikelegalanddesignwasaround1.2 billion last year. Among all AI application domains, healthcare ranks second only to chatbots and code generation in growth speed. This capital surge has already spawned 8 healthcare AI unicorns and numerous growth-stage companies valued between 500millionand1 billion—more than in legal, financial, media, or any other vertical AI sector.
Take the medical documentation segment—the most capital-intensive and mature—as an example. OpenEvidence and Abridge represent two archetypal models. OpenEvidence, backed by top-tier investors like GV and Sequoia and founded by serial entrepreneurs, leads in valuation. Abridge, founded by clinicians and heavily invested in by a16z, has built exceptional clinical trust through its large-scale GenAI deployments and is widely recognized as an industry benchmark.
As the technology matures, medical documentation companies are extending beyond single-function offerings into longer value chains. Ambience has expanded from ambient dictation into medical coding and revenue management, showing platform-like tendencies. SmarterDx focuses on improving coding accuracy, while Commure specializes in hospital revenue cycle management. Meanwhile, EliseAI enters from front-office scenarios like patient communication and billing, aiming to systematically software-enable highly manual service workflows and unlock larger service-budget allocations.
Next-generation AI companies are also demonstrating structural influence. On the payer side, Distyl represents early exploration of deep AI collaboration between providers and payers. On the service side, Hippocratic AI, centered on the principle of “non-maleficence,” focuses on care navigation and patient interaction, attempting to define a new AI-driven care delivery model. Together, these companies form the core force accelerating the evolution of the healthcare AI ecosystem.
AI Adoption in Healthcare Is “Non-Linearly Accelerating”
Healthcare is now entering a critical phase of AI race, with leading institutions deploying AI at unprecedented scale and speed.
Kaiser Permanente, the oldest integrated non-profit health system in the U.S. (founded in the 1940s), has deployed Abridge’s Ambient Documentation system across 40 hospitals and over 600 outpatient clinics nationwide—the largest generative AI implementation in healthcare history and Kaiser’s fastest technology rollout in the past 20 years.
Advocate Health, a major multi-hospital system, evaluated over 225 AI solutions and selected 40 for large-scale deployment, including Microsoft Dragon Copilot, Aidoc, Rad AI for imaging analysis, and intelligent call centers. These are expected to cut documentation time by over 50% and automate prior authorization, referrals, and coding.
Mayo Clinic, a century-old global leader in academic medicine and research, announced plans to invest over $1 billion in more than 200 AI projects over the next few years, spanning administrative automation to diagnostic and clinical decision support—pursuing a balanced “operations + clinical” AI transformation.
SimonMed, one of the largest independent radiology groups in the U.S., has expanded its AI partnerships from fewer than 10 to over 50, covering core processes from patient registration and smart dictation to revenue cycle management—reflecting AI’s evolution from “functional tool” to “systemic orchestration.”
Grow Therapy, a fast-growing digital mental health platform, is pioneering a new path by developing AI care companions that use voice and language analysis to replace static assessment scales (e.g., PHQ-9, GAD-7), enabling real-time mental state monitoring and 24/7 support.
Unlike traditional healthcare IT projects—which often took years for evaluation, procurement, and deployment—generative AI tools are now moving from pilot to enterprise-wide rollout in just months, far outpacing historical norms.
This shift stems first from a change in deployment logic. New-generation healthcare AI products are typically delivered as SaaS or APIs embedded into existing systems, eliminating the need for massive IT overhauls and significantly reducing implementation costs and organizational resistance. Moreover, these tools directly enhance high-frequency, mission-critical workflows—such as clinical documentation, coding, prior authorization, and patient communication—enabling clear, short-cycle ROI quantification and lowering executive decision thresholds.
Industry leaders like Mayo Clinic, Cleveland Clinic, and Kaiser Permanente are validating this “fast and precise” model. When selecting AI partners, they prioritize three criteria:
Technical maturity and scalability: Preference for ready-to-deploy solutions proven to operate reliably at scale, avoiding lengthy, high-risk custom development.
Risk stratification and patient contact level: Back-end or non-patient-facing administrative functions can launch faster; clinical decision or patient-interaction applications require rigorous validation and ethical review.
Short-term value and trust building: Applications delivering measurable results quickly help build internal confidence and external credibility, creating a positive feedback loop for broader adoption.
Notably, cost is not the primary consideration. In healthcare AI, failure carries consequences beyond financial loss—it risks operational disruption, patient safety, and reputational damage. Thus, institutions are often willing to pay a premium for safe, reliable, and validated solutions to ensure system stability and trustworthy outcomes.
In other words, AI in healthcare is no longer just a symbol of technological innovation—it’s becoming a defining factor of organizational competitiveness. The “rapid experimentation + continuous iteration” model is reshaping how healthcare organizations approach technology procurement. Surveys show procurement cycles are shortening significantly:
Health systems reduced traditional IT procurement from 8.0 to 6.6 months (18% faster).
Outpatient providers shortened cycles from 6.0 to 4.7 months (22% improvement).
In contrast, payer procurement cycles lengthened from 9.4 to 11.3 months, while pharma/biotech remained around 10 months.
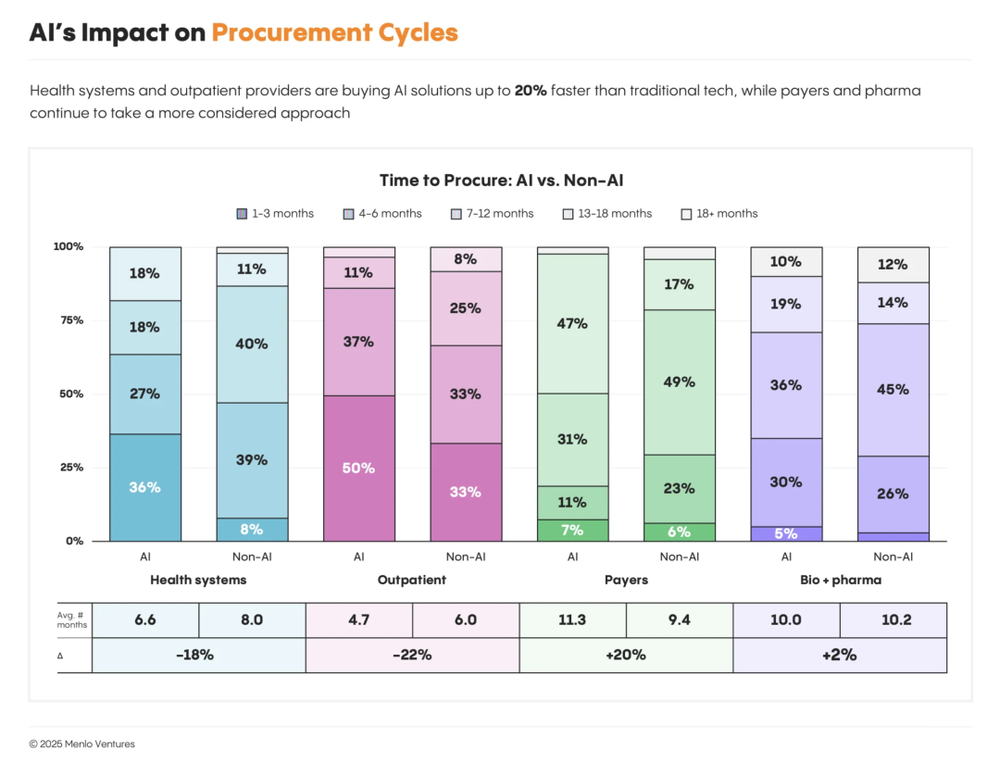
This divergence reflects differences in AI awareness and application depth. Previously seen as slow adopters (some startups even called them “pilot black holes”), providers have now crossed the trial threshold and are scaling AI into production. Payers and biopharma remain in exploratory phases—“curious but cautious”—largely confined to proof-of-concept or small experiments.
In short, health systems are proving through action: AI is no longer just a future trend—it’s a current competitive imperative.
02. The New Landscape of Healthcare AI Investment and Financing
Where Is AI Budget Going?
The pace of capital inflow mirrors AI’s adoption rhythm in healthcare. Of the total $1.4 billion in healthcare AI investment:
Health systems: ~$1 billion (75%)
Outpatient providers: $280 million (20%)
Payers: $50 million (~5%)
Biotech/life sciences: minimal
This distribution isn’t accidental. Health systems face low margins, heavy workloads, high administrative costs, and severe staffing shortages—making AI’s ROI direct and measurable. AI is becoming the key tool to break through efficiency bottlenecks and cost constraints.
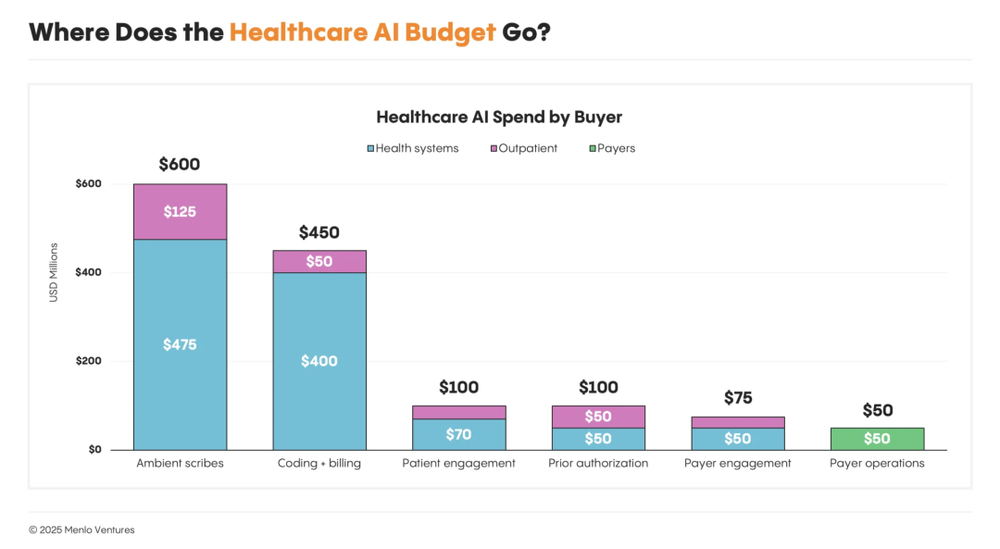
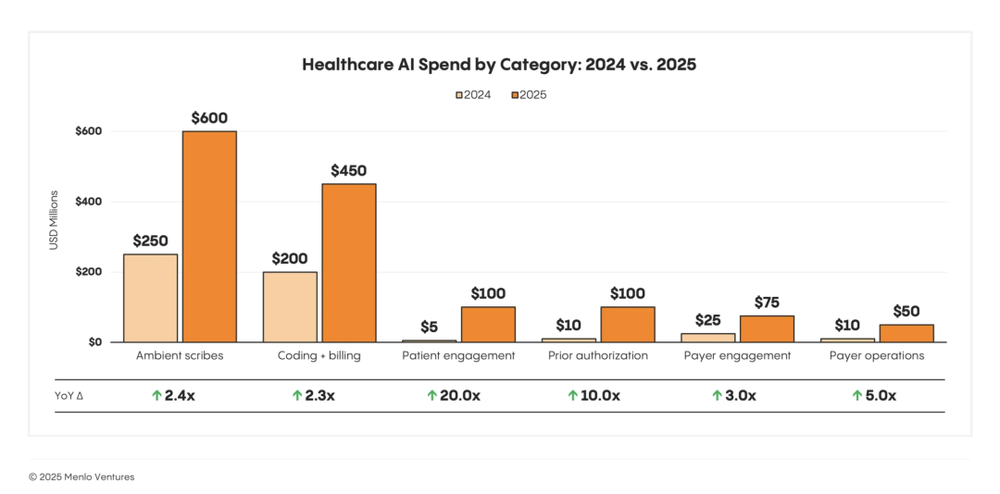
Two AI application categories are attracting capital most rapidly:
Ambient Clinical Documentation: ~$600 million annually. Reduces physician burnout and documentation burden. Companies like Abridge use voice recognition + GenAI to convert conversations into clinical notes and populate EHRs.
Coding & Billing Automation: ~$450 million annually. Reduces coding errors and claim denials to boost revenue.
Additionally, two emerging areas are growing fastest:
Patient Engagement: 20x YoY growth—enhancing care adherence and interaction.
Prior Authorization: 10x YoY growth—automating payer approval workflows.
Patient engagement refers to using digital and AI tools to improve communication, health behavior adherence, and experience across the care journey—including scheduling, follow-ups, Q&A, and health management.
Prior authorization is the process where providers must submit documentation to insurers for approval before certain treatments, tests, or prescriptions—a traditionally slow, manual, error-prone process.
Clearly, AI investment is shifting from “conceptual capital” to “performance capital”—flowing to areas that quickly boost efficiency, revenue, and patient experience. Healthcare AI is no longer experimental—it’s a key engine for financial optimization and operational upgrade.
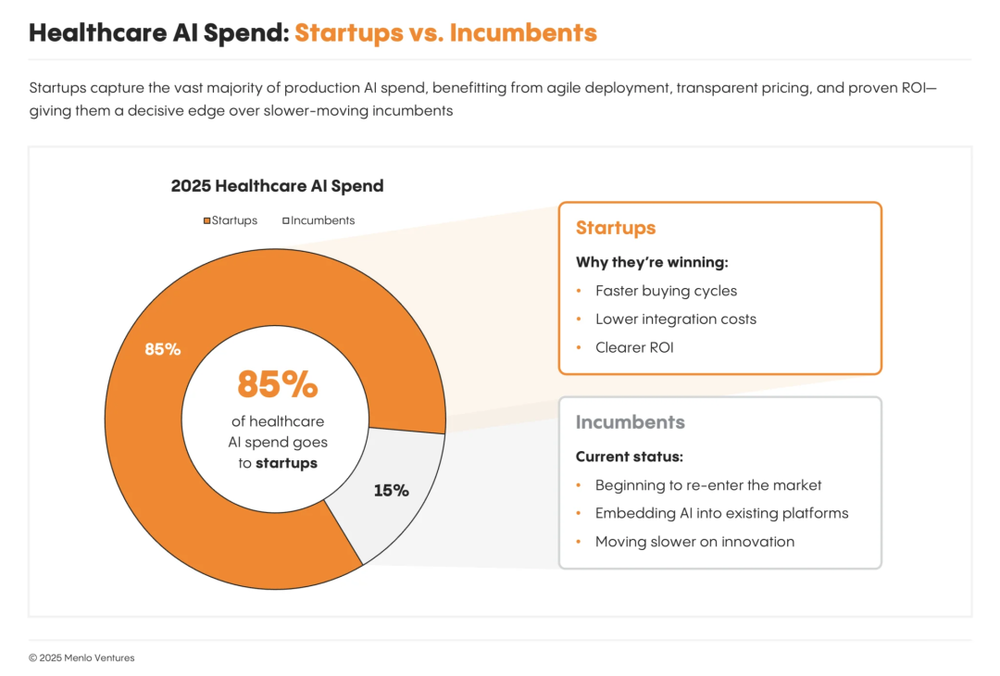
85% of GenAI Spending Goes to Startups
Currently, 85% of all generative AI spending in healthcare flows to startups—not legacy giants. Even in mature segments like ambient scribing, where Microsoft’s Nuance DAX is deployed in 77% of U.S. hospitals, startups like Abridge and Ambience are capturing nearly 70% of new market share due to superior performance.
Why? Startups move faster, build AI-native products from the ground up, and aren’t burdened by legacy tech debt or corporate bureaucracy. In contrast, incumbents often bolt AI onto old platforms as add-ons. Thus, AI-native firms gain adoption and market share more quickly.
For EHR giants like Epic, Oracle Health, athenahealth, and Change Healthcare, this marks the onset of true disruption. Many AI-native solutions start with a single entry point (e.g., scribing) and expand functionality—potentially replacing core systems of incumbents. Yet traditional players are fighting back using their advantages in distribution, integration, and scale.
AI-Powered Services Are an Emerging Frontier
Healthcare AI spending isn’t limited to IT budgets—service budgets are also gaining investor attention. As AI penetrates front-end service scenarios like patient communication, health management, and prior authorization, service-type budgets are becoming a new investment focus.
Unlike traditional IT hardware/software expenses, service budgets cover operational costs, training, and staffing. Companies like Abridge and Ambience not only charge for EHR integration but also co-invest in training, operational support, and workflow optimization with providers. Thus, AI spending is shifting toward service budgets—a new frontier for capital.
03. Providers: The Earliest, Largest, and Highest-ROI AI Application Arena
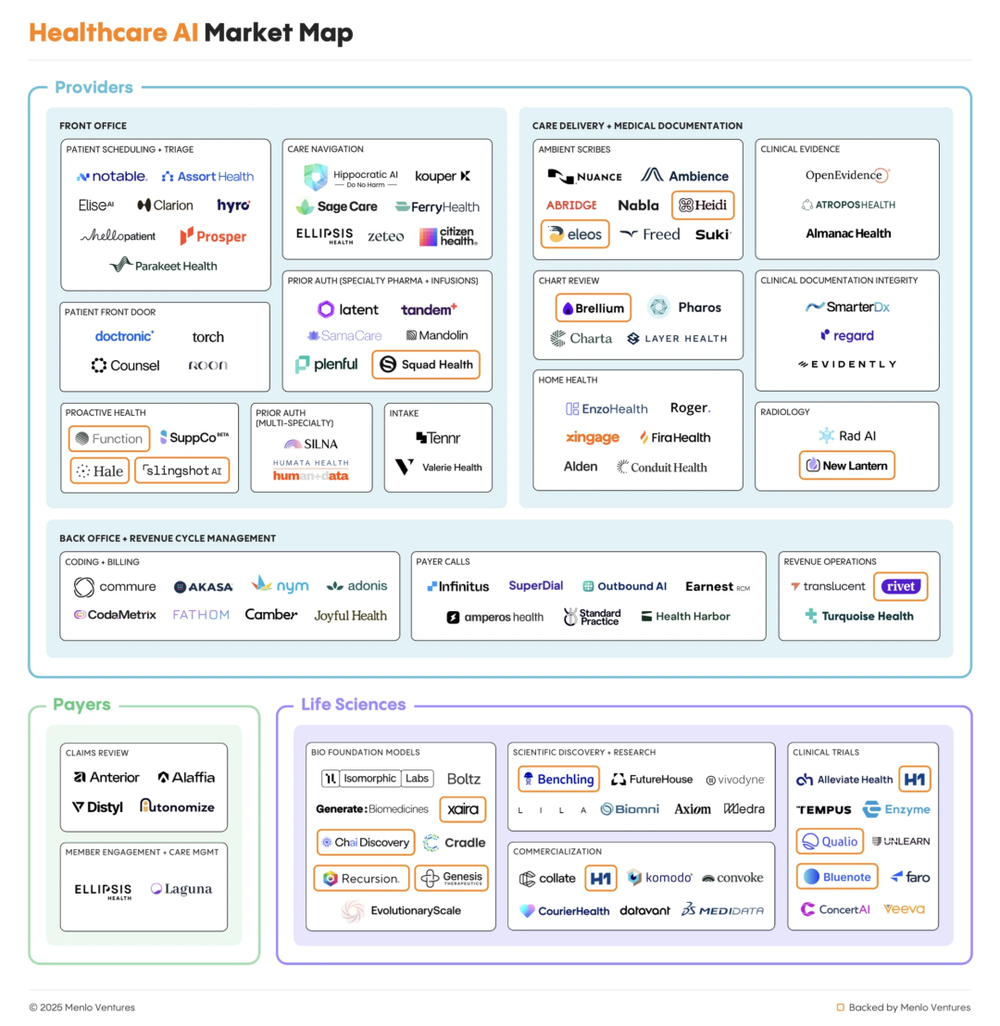
IT Use Cases: Clinical Documentation & RCM
Clinical/administrative documentation includes all records generated during care—medical notes, reports, orders, and supporting documents for billing and audits.
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) encompasses the end-to-end administrative and financial workflow—from patient registration and prior authorization to coding, billing, insurance claims, and final payment.
Total spending on documentation and back-end RCM is ~$38 billion, representing ~60% of healthcare IT expenditure:
Clinical Documentation: $19.6B (30% of IT spend)
Back-end RCM: $18.8B (29% of IT spend)
Companies like Abridge, OpenEvidence, Commure, and Smarter Technologies are competing for this existing spend—not to replace Epic or Waystar, but to enhance them via intelligent automation, reducing human effort in clinical and administrative tasks.
This “integration-first” strategy offers a clear path to scale: AI becomes an intelligent layer between clinicians and EHRs, billing teams and claims processors. From there, they can horizontally expand into adjacent modules, gradually penetrating underlying systems and challenging traditional record-keeping platforms.
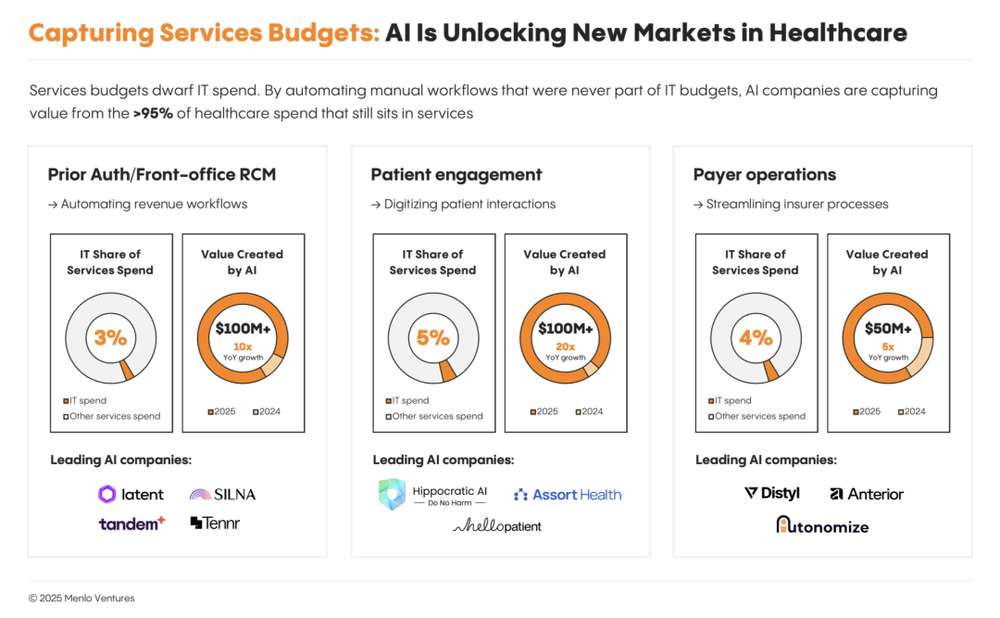
Of the $740 billion total spent on healthcare administration, software/SaaS represents a tiny fraction. Beyond traditional IT budgets lies vast untapped potential in previously non-automatable administrative services—like prior authorization, patient communication, and front-office RCM. These are typically handled by nurses, front-desk staff, or outsourced teams, funded by service budgets, not IT.
Prior Authorization
Widely regarded as one of healthcare’s most complex, time-consuming, and contentious administrative processes, prior authorization is also the most ripe for AI disruption. Front-office RCM-related administrative spending totals ~$98 billion annually, yet only ~3% is software-enabled.
Traditionally, registration and electronic authorization rely on manual form-filling. Clinicians must extract unstructured data from EHRs, apply clinical judgment, and reformat it per insurer requirements—a process taking days or weeks, prone to errors.
Generative AI is automating this. Companies like Latent Health, Tandem, Mandolin, and Squad Health enable approvals in minutes instead of days—reducing treatment delays, improving patient experience, and freeing clinician capacity.
The Full Patient Journey
Efficiency bottlenecks concentrate at the beginning and end of care. Patients struggle to access appropriate resources initially, and post-treatment follow-up suffers from fragmented communication, harming adherence and outcomes. These tasks have long relied on nurses or call centers—inefficient and costly.
AI is now optimizing the entire patient journey:
Real-time health management: Function Health, Ash, SuppCo use biomarker tracking and lifestyle data for daily health management.
AI triage & symptom assessment: Doctronic, Counsel Health, Torch Health, Roon use voice/text to assess symptoms and route patients appropriately.
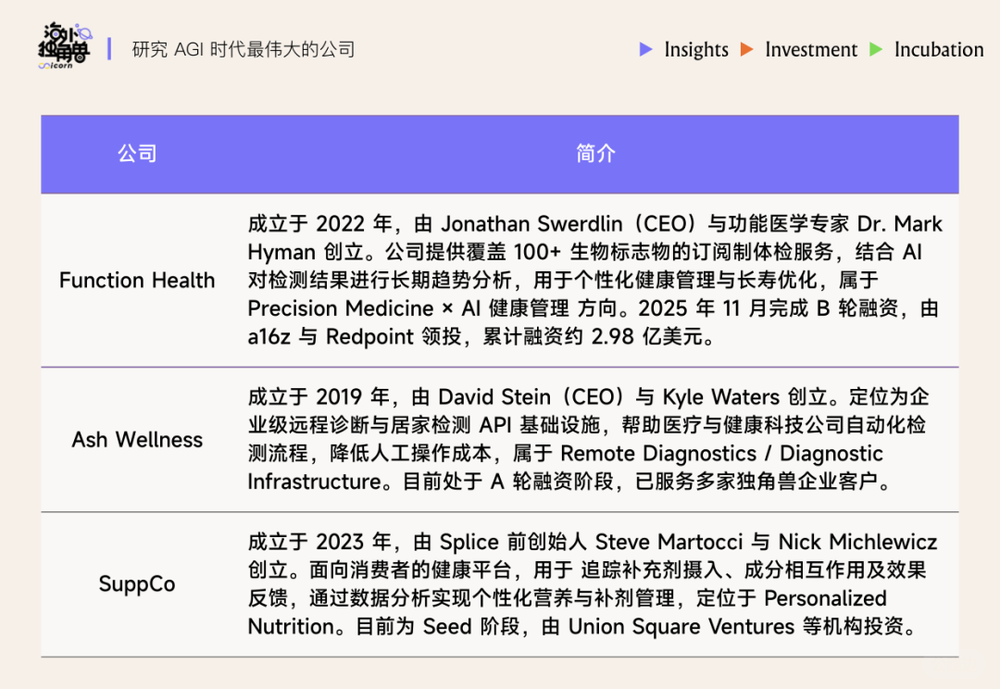
Appointment & workflow automation: Assort Health, Hello Patient, Clarion automate scheduling and triage.

Care navigation & follow-up: Hippocratic AI, Ellipsis Health, Kouper Health, Ferry Health, Solace Health manage communication, result delivery, appointments, and follow-ups—ensuring continuity.

04. AI in Payer Operations: Early-Stage but Growing Rapidly

Payers—typically health insurers or managed care organizations—pay for healthcare services.
The AI market in payer operations has surpassed $50 million, growing at 5x annually. Key players include Distyl, Anterior, and Autonomize.
Though payer procurement cycles are long (~1 year) and enterprise requirements stringent, AI remains early-stage. Yet potential is vast—in prior authorization, utilization management, payment integrity, and risk adjustment. In the future, provider-side AI agents may directly interface with payer-side agents, creating end-to-end intelligent workflows that reduce administrative friction, lower costs, and shorten treatment delays.
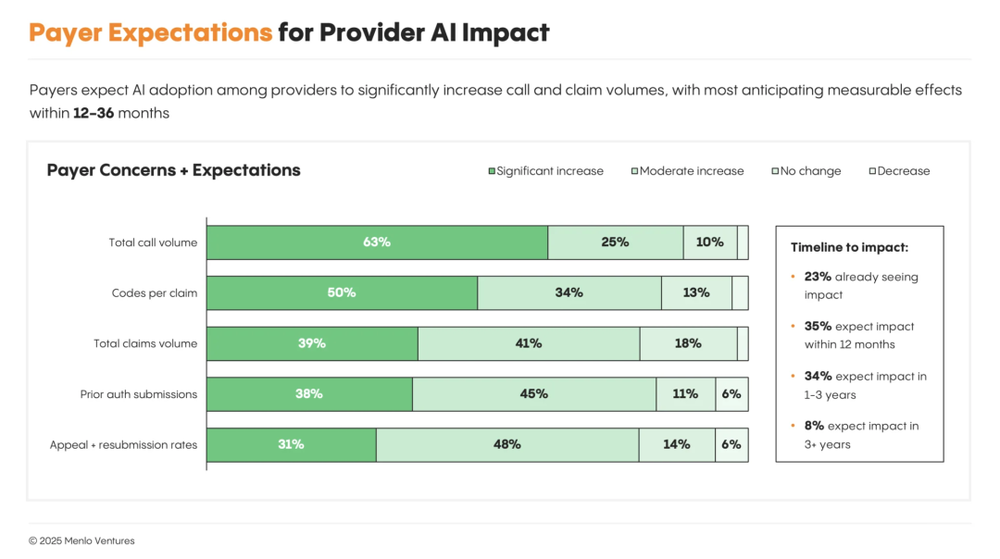
However, as providers deploy AI at scale, payers face two systemic frictions:
Operational overload: AI-powered automation drastically increases claim submissions, inquiries, and appeals—risking overwhelming manual review systems and exposing bottlenecks.
Cost inflation & payment risk: LLM-based coding systems identify missed billable items and optimize reimbursement structures, increasing provider revenue—but raising payer concerns about inappropriate payments and the tension between faster approvals and cost control.
In response, some payers are adopting defensive strategies:
Tightening medical necessity policies
Strengthening audit mechanisms
Issuing AI usage compliance guidelines for providers
Partnering with platforms like Distyl to deploy counterbalancing AI systems
Overall, payer strategy remains in a transitional “observe, test, defend” phase—lacking industry standards, with ecosystem dynamics evolving rapidly.
05. The Rise and Platformization of AI Scribes
AI Scribes automatically generate clinical documentation by capturing doctor-patient conversations (live or recorded) and producing structured outputs like SOAP notes, discharge summaries, etc.—dramatically reducing physician paperwork.
AI Scribes: Among the First Commercialized Segments
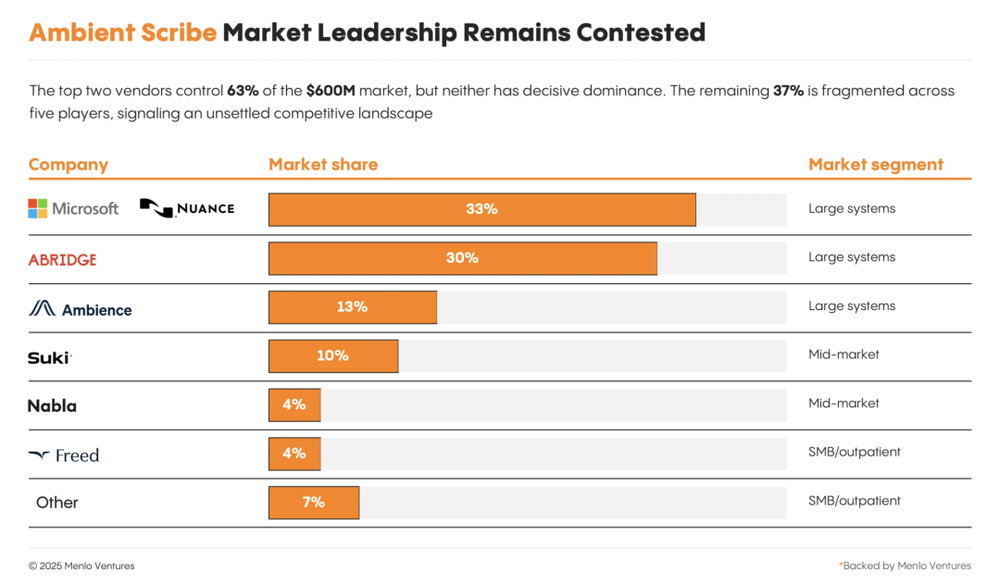
Ambient Scribe is one of the earliest commercially successful AI categories in healthcare. By 2025, the market is projected to reach $600 million—2.4x growth YoY—leading all clinical AI applications in revenue and attention. Two unicorns have emerged: Abridge (~30% market share) and Ambience (~13%). However, Nuance’s DAX Copilot still leads slightly at ~33%.
Nuance
Acquired by Microsoft for $19.7B in 2022, Nuance is the de facto leader in AI Scribing. DAX Copilot integrates GPT-4 and Azure OpenAI, natively embedding into EHRs like Epic for automated ambient documentation. Its strength lies not in rapid innovation but in stability, compliance, and deep integration with existing healthcare IT infrastructure. Microsoft’s channel and customer base provide strong defense, though slower product iteration leaves room for agile startups.
Abridge
Founded in 2018 by clinicians and academics, Abridge emphasizes generating “trustworthy” clinical documents. Its key differentiator is traceability: physicians can click any generated note to review the original audio snippet—mitigating hallucination risks. Strong noise reduction and domain-specific LLM fine-tuning enhance real-world usability. Abridge has gained strong clinician trust and entered major health systems—but faces challenges in scaling delivery quality and competing on price/channel against giants.
Ambience Healthcare
Founded in 2020, Ambience positioned itself early as an “AI operating system for physicians,” going beyond documentation. Its platform covers coding suggestions, documentation optimization, referral support, and patient education—with specialty-specific customization and real-time prompts. This full-workflow approach resonates with specialty clinics and mid-sized providers, though added complexity raises integration and learning costs.
Ambient Scribe’s value is intuitive: for every 5 hours of patient care, physicians spend 1 hour on documentation. AI Scribes act as “aural assistants,” converting conversations into structured EHR entries—freeing doctors from keyboards and delivering the most direct productivity gains in healthcare AI.
Yet two constraints threaten sustained growth:
Market saturation: Large systems estimate ambient scribe penetration at ~35%, rising only to ~40% in three years. Growth among small practices is slowing.
Low stickiness: Among large systems, willingness to switch vendors nearly equals loyalty; in outpatient settings, 67% plan to switch. Customers view scribing as commoditizing, with low switching costs.
Thus, staying as a “document copier” won’t sustain long-term competitiveness.
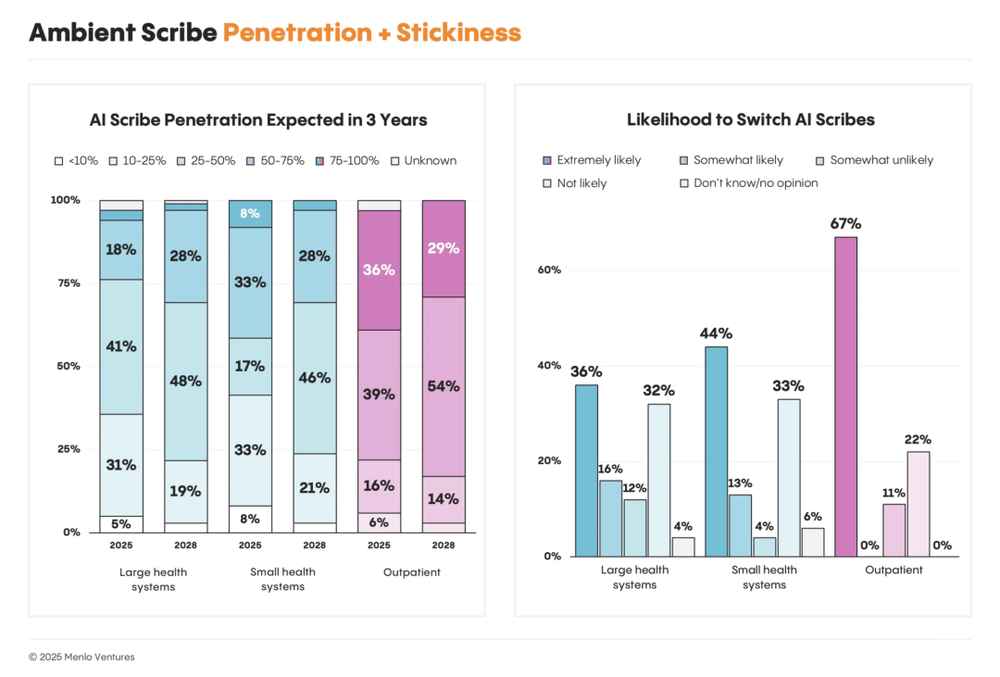
Scribes and EHRs Are Forming Scenario-Based Division of Labor
These constraints explain why many startups are evolving into platforms—becoming healthcare AI hubs, not just note-takers.
Abridge partnered with Highmark Health to apply AI to real-time prior authorization.
Ambience expanded into revenue integrity and medical coding.
Nabla, Freed, Eleos Health (behavioral health leaders) added compliance and back-office RCM modules.
Meanwhile, EHR giants are responding. Epic, Oracle Health, and athenahealth recently launched native ambient scribing tools, embedding AI directly into core platforms.
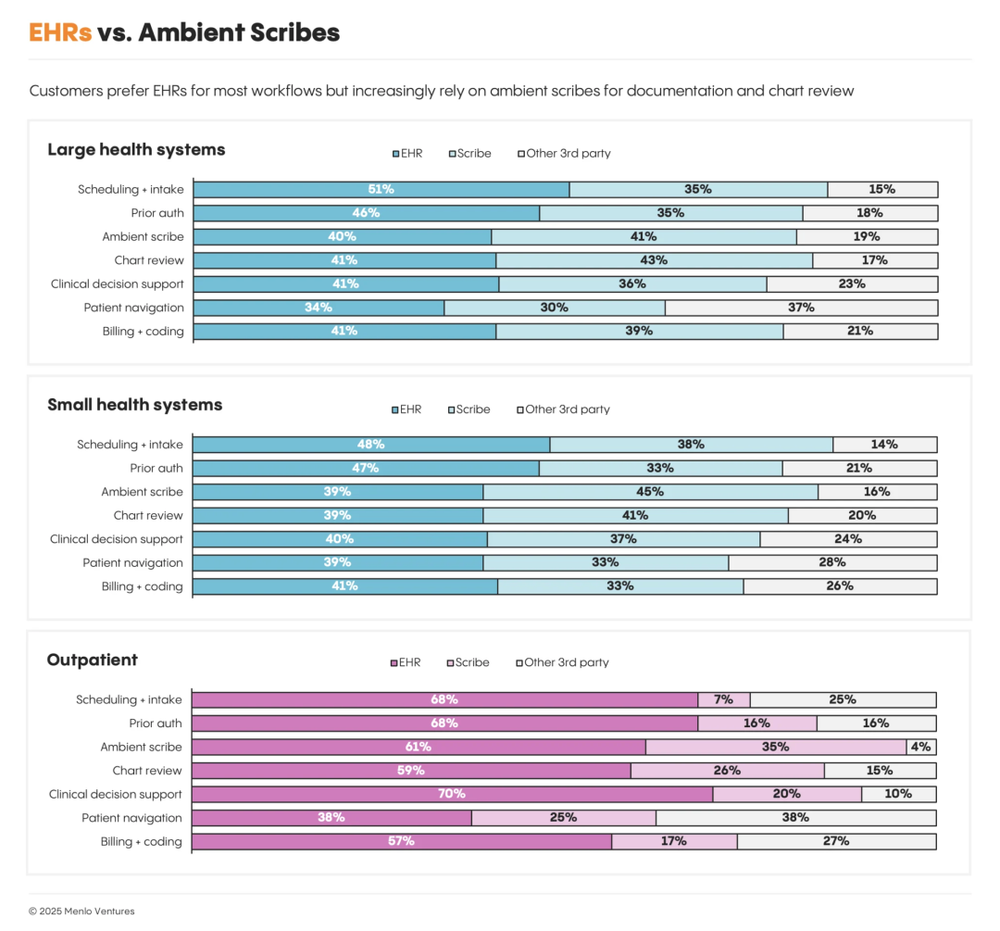
Usage patterns reveal a clear division:
Third-party ambient scribes (like Abridge) rival EHR-native tools in large systems for core clinical documentation, indicating strong clinical acceptance.
But for scheduling, prior auth, CDS, patient navigation, coding, and billing, EHRs dominate—especially in outpatient settings—due to workflow integration, data consistency, and compliance trust.
Menlo’s survey shows: while 85% of AI revenue goes to startups, most customers prefer buying AI through their existing EHR platforms. Startups compete in “ambient scribing” and “note review,” but EHRs lead in coding, billing, prior auth, scheduling, CDS, and navigation.
This preference isn’t fixed. If startups consistently deliver higher efficiency and ROI, customer choices could flip in coming years. But for now, incumbents’ distribution networks and relationship moats remain formidable.

06. Key Growth Areas for AI Healthcare in the Next 3–5 Years
AI in Life Sciences: Still in R&D Validation and Early Deployment
Unlike provider-side immediacy, life sciences (pharma/biotech) AI is in a dual-track phase of “R&D validation + initial deployment.” Most companies are exploring AI’s systemic feasibility across drug development.
Key adoption areas include:
R&D data analysis (63%): automating public/experimental data parsing for feature extraction and experiment design.
Quality & compliance (48%): Veeva, Qualio, Enzyme drive automated regulatory documentation.
Preclinical research (42%): Axiom, Vivodyne accelerate molecular screening and in vitro validation.
Medical affairs & clinical trials (~40%): Tempus, Unlearn, ConcertAI streamline trial processes and evidence generation.
Notably, 66% of pharma companies are building proprietary models to secure data advantage and IP—signaling a strategic shift from “using models” to “building models.” Companies like Xaira, Evolutionary Scale, and Chai Discovery are developing “Biology Foundation Models” for various biological systems, aiming to transform drug discovery from experiment-intensive to data-driven.
AI in life sciences is also expanding beyond R&D into manufacturing and commercial functions—process optimization, quality monitoring, regulatory submission automation, market access, and commercialization—marking the sector’s entry into full-stack AI transformation.
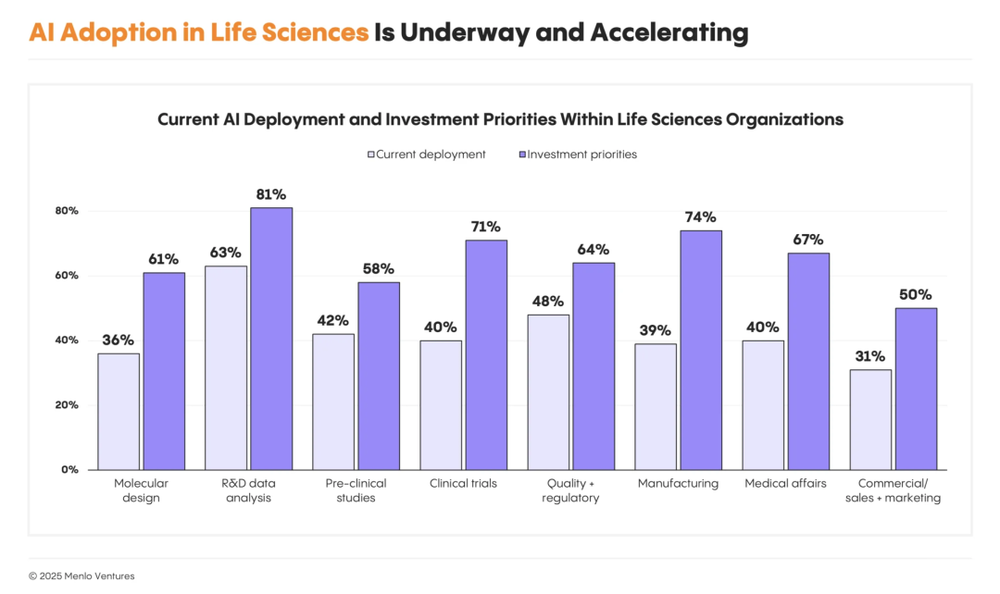
The AI Era in Healthcare Has Arrived
AI is no longer a lab concept—it’s a tangible force improving efficiency and care quality. Providers are witnessing quantifiable returns: peer adoption, lower costs, better patient experiences. Procurement cycles have shortened from 12–18 months to under 6. The conditions for AI’s rapid growth are fully mature.
Yet ~80% of the potential market remains untapped. Next-phase growth will come from:
Service budget automation: AI-redesigned admin workflows to free human capacity.
Intelligent voice & patient interaction: end-to-end AI companions across pre-, during, and post-visit.
Prior authorization optimization: AI-accelerated payer approval chains to reduce wait times.
Intelligent drug discovery: foundation models and proprietary algorithms driving R&D leaps.
These are healthcare AI’s next “gold mines”—set to reshape the industry over the next 3–5 years.
Reference
2025: The State of AI in Healthcare|https://menlovc.com/perspective/ ... f-ai-in-healthcare/
|